Research: Sustainability by Catalysis
Sustainable Syntheses
Contact: torsten.irrgang@uni-bayreuth.de
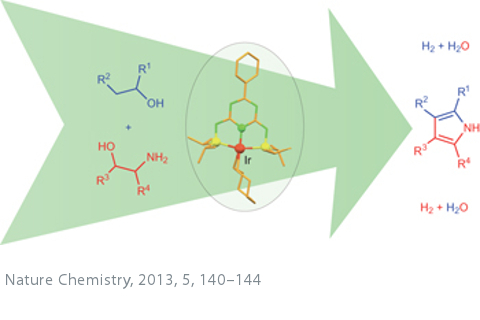
The development of novel catalytic reaction, in which alcohols are converted into important classes of compounds, contributes to the saving of our fossil carbon resources and the lowering of CO2 emission since alcohols can be obtained from indigestible and abundantly available biomass such as lignocellulose. The aims of this project are the rational design of such reactions and of catalysts mediating them.
Earth Abundant Transition Metal Catalysis
Contact: torsten.irrgang@uni-bayreuth.de
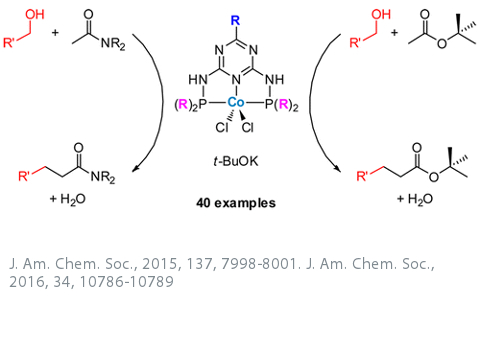
The conservation of our element resources is of outmost importance with regard of the future of mankind. One approach to save rare elements is their replacement by abundantly available elements in key technologies. Catalysis is a key technology and often mediated by rare noble metals. We are interested in replacing noble metals such as Pt, Pd, Ir, Rh or Ru by so called base metals (Co, Fe and Mn) in catalysis. Homogenous catalysis is used to explore the scope of such a replacement and to develop novel catalytic reactions mediated by base metals.
Polymer Derived Ceramic Base Catalyst Support
Contact: christine.denner@uni-bayreuth.de
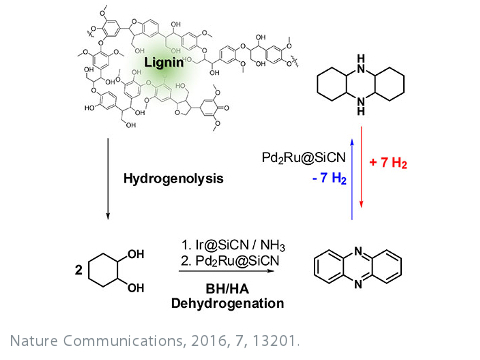
Polymer derived silicon carbon (nitride) [SiC(N)] ceramics exhibit interesting catalysis relevant properties such as high thermal stability, great resistance against chemicals and structuring at multiple lengths scales. When modified with metals, such a material could be employed as a heterogeneous catalyst. The aim of the project is the development of the catalyst class and applications of the catalysts in sustainable synthesis and energy storage.
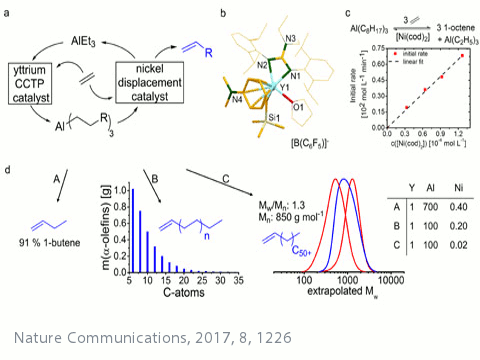
Polymerization Catalysis
Contact: winfried.kretschmer@uni-bayreuth.de
We have a strong interest in the controlled and efficient polymerization of ethylene and novel products accessible by such controlled polymerization processes. In addition, we are intrested in novel on-demand olefin syntheses.
Research Programs